CVS / Amniocentesis test
- TOP
- Our Services and
- CVS / Amniocentesis test
What is CRIFM CVS / Amniocentesis test?

There are many possible chromosomal abnormalities, ranging from minor ones that have little or no effect to those that can affect the growth of the fetus' body and brain.
The CVS / Amniocentesis test of CRIFM is a test performed to confirm the diagnosis by collecting chorionic tissue and amniotic fluid when chromosomal diseases or genetic diseases are suspected by ultrasonography.
At CRIFM, the first step is to have a fetal diagnosis, which is a detailed ultrasound examination of the fetus. Then, only if there is a possibility of chromosomal abnormalities, we will ask the patient to consider chorionic examination and Amniocentesis.
After the test, the results can be provided within a day at the earliest using the QF-PCR method for rapid determination of Down syndrome, 13-trisomy and 18-trisomy. Another advantage of CRIFM is that it can detect microchromosomal abnormalities, which have recently been discovered in many pediatric fields.
Dr. Pooh is one of the best in Japan at performing more than 80% of the CVSs performed in Japan, and with over 13,000 cases under her belt, the risk of miscarriage from the CVS / Amniocentesis test is less than 0.1%. The risk of miscarriage by CRIFM's CVS / Amniocentesis test is less than 0.1%, which is one of CRIFM's strengths.
*The general risk of miscarriage is said to be 0.2 to 0.3%.
CRIFM is also unique in its ability to detect micro-anomalies in all chromosomes. D-karyo (digital chromosome), which uses the most advanced next-generation sequencing technology, can detect microstructural abnormalities (microdeletions and duplications) that are not visible in G-band.
Risks of CVS / Amniocentesis test
CVS and Amniocentesis test are performed by inserting a needle into the mother's abdomen to collect villi and amniotic fluid from the uterus.
At our clinic, we explain the risks involved and only perform the test if the patient agrees to it. In addition, we pay close attention to the maternal blood test and the handling of equipment to ensure the safety of the test.
*The general risk of miscarriage is estimated to be 0.2-0.3%, but with CRIFM it is less than 0.1%.
The CVS/Amniocentesis test is a definitive test for chromosomal abnormalities. Diagnosis of microchromosome aberrations was not available until 2019, but will be available from March 2020. Currently, all CVS/Amniocentesis test for microchromosome aberrations are performed at D-karyo.
The CVS may show placental focal mosaicism, which is a chromosomal abnormality only in the placenta. In this case, a further Amniocentesis test should be done to check whether the baby has the mosaicism or not.
Difference between CVS / Amniocentesis test of CRIFM
| Chorionic villus test | Amniocentesis test | |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection Period | 11-13 (~17) weeks | After 16 weeks |
| Time to rapid results and karyotype results | Rapid results in 0.5-1 day Karyotype results in 14-21 days |
|
| puncture site | Maternal abdominal wall | |
| Specimens to be collected | villus | amniotic fluid |
| Original cells of the collected specimen | Nutritional Ectoderm (TE) | Inner cell mass (ICM) |
| Membrane to be punctured | villus | Chorionic membrane and amnion |
| Size of puncture needle | 18 / 20gauge | 25gauge |
| local anesthesia | Necessary | unnecessary |
| Possible contact with the fetus or umbilical cord | None | Yes |
| Procedure-related risk of miscarriage | 0.2% | 0.3% |
| Risk of miscarriage(compared to groups with the same risk) | -0.11% | 0.12% |
| Placental-localized mosaic(CPM) | 0.5-1.0/100* | None |
* Data at the CRIFM Prenatal Medical Clinic
* https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/uog.20410
What is a CVS?
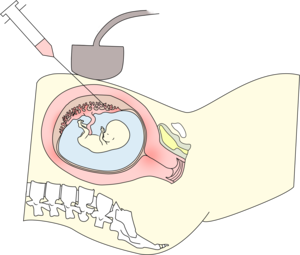
The CVS is a genetic test for chromosomal abnormalities that can be done at 11-13 weeks (14-17 weeks are also possible) of pregnancy. The chorionic villus is collected from the mother's abdomen using a transabdominal double-needle technique with clean hands.
The procedure is performed with as much safety as possible while looking at the uterus by transabdominal ultrasonography. A small amount of local anesthetic is used, but it is thought to have little effect on the fetus. However, please consult us if you have any concerns.
The CVS takes about 10 seconds. If an unpredictable situation arises, we will do our best to deal with it according to the situation.
Features of the CRIFM CVS
The risk of miscarriage with the CVS is generally said to be 0.2%, but at our clinic it is less than 0.1%. In addition to performing the test with less risk, we take every possible precaution.
In addition, chorionic tissue, which contains cells of fetal origin, is collected and the fetal DNA is extracted for testing. The results for Down's syndrome, 18-trisomy, and 13-trisomy can be obtained in one day, but it takes about 2-3 weeks to obtain the G-band result, which confirms the presence or absence of an abnormality, and the D-karyo result, which looks at microchromosomal abnormalities, by collecting cells from the amniotic fluid, culturing them to increase the number of cells, and then examining the shape and number of chromosomes.
CVS flow
In order to ensure the safety of the CVS, CRIFM will first check the mother's blood for white blood cells and CRP to make sure that there is no infection in the mother. If the results are positive, we will postpone the CVS.
If there is no problem after the maternal blood test, local anesthesia will be administered, and the chorionic tissue will be harvested with great care and safety while being confirmed by transabdominal ultrasonography. The test takes about 10 seconds.
After the CVS, you will be asked to rest for about 15-20 minutes, and then go home after the ultrasound examination confirms that the fetus is healthy.
CVS fee
| CVS fee (including QF-PCR rapid test, chromosome karyotyping and D-karyo microchromosome test) |
229,900 yen (tax included) |
|---|---|
| preoperative scan | 5,500 yen (tax included) |
| DNA extraction cost | 16,500 yen (tax included) |
| Explanation of results and genetic counseling | 3,850 - 22,000 yen (tax included) |
*In addition to the above basic fees, fetal diagnosis: 41,800 yen (including tax) will be charged for those who have not yet undergone fetal diagnosis.In addition, the following fees will be charged: initial application fee: 3,080 yen (tax included) / without a letter of introduction from your doctor: 5,500 yen (tax included) / SNPmicroarray test: 110,000 yen (tax included) / Whole Exome Sequencing: 418,000 yen (tax included) / special FISH test: 49,500 yen (tax included) Special FISH test: 49,500 yen (including tax) / Medical Information Form: 8,800 yen (including tax) / Coordination with other facilities: 5,500 yen or more (including tax)
What is Amniocentesis test?
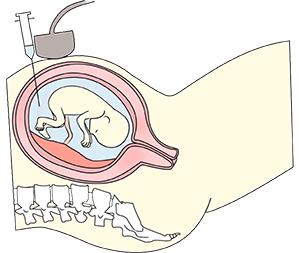
The Amniocentesis test involves collecting amniotic fluid from the mother's abdomen in a clean operation.
The transabdominal ultrasound is used to view the inside of the uterus, avoiding the uterine blood vessels, fetal umbilical cord and placenta for safety.
The examination takes about one minute.
Features of the CRIFM Amniocentesis test
The Amniocentesis test is a genetic test for chromosomal abnormalities done after the beginning of 16 weeks. The results for Down's syndrome, 18-trisomy, and 13-trisomy can be obtained in one day, but it takes about 2-3 weeks to obtain the G-band result, which confirms the presence or absence of an abnormality, and the D-karyo result, which checks for microchromosomal abnormalities.
The risk of miscarriage or water breakage during Amniocentesis test is generally said to be 0.3%, but in our clinic, the risk is less than 0.1%. We take the utmost care to ensure that the Amniocentesis test can be performed safely with less risk.
If an unforeseen situation arises, we will do our best to deal with it according to the circumstances.
Flow of the Amniocentesis test
In order to make sure that you can safely undergo the Amniocentesis test, we will first check your mother's blood for white blood cells and CRP to make sure that there is no infection in your mother. If you test positive, we will postpone the Amniocentesis test date.
If there are no problems after the maternal blood test, a transabdominal ultrasound is used to view the inside of the uterus and carefully collect the sample, avoiding the fetus, umbilical cord, and placenta. No anesthesia is required and the examination takes about one minute.
After the examination, you will be asked to rest for about 20 to 30 minutes, and then go home after the ultrasound examination confirms that the fetus is healthy.
Fees for Amniocentesis test
| Amniocentesis test fee (including QF-PCR rapid test, chromosome karyotyping and D-karyo microchromosome test) |
189,900 yen (tax included) |
|---|---|
| preoperative scan | 5,500 yen (tax included) |
| DNA extraction cost | 16,500 yen (tax included) |
| Explanation of results and genetic counseling | 3,850 - 22,000 yen (tax included) |
*In addition to the above basic fees, fetal diagnosis: 41,800 yen (including tax) will be charged for those who have not yet undergone fetal diagnosis.In addition, other fees may be required, such as initial application fee: 3,080 yen (tax included) / without referral letter from attending physician: 5,500 yen (tax included) / SNPmicroarray test: 110,000 yen (tax included) / Whole Exome Sequencing: 418,000 yen (tax included) / Special FISH test: 49,500 yen (tax included) / Medical Information Form: 8,800 yen (tax included) / Coordination with other facilities: from 5,500 yen (tax included)
For both the CVS and the Amniocentesis test, mothers and fathers are required to come to the clinic together to explain the test results. If you are not able to come to the clinic together for the explanation of the results, you will not be able to take the test.
What is a chromosomal abnormality?
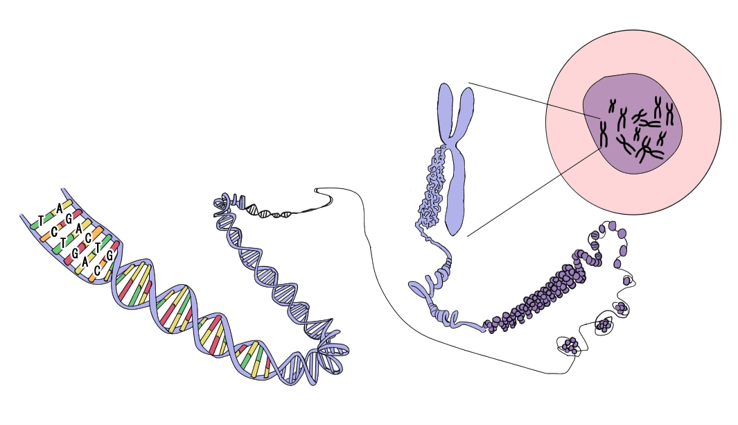
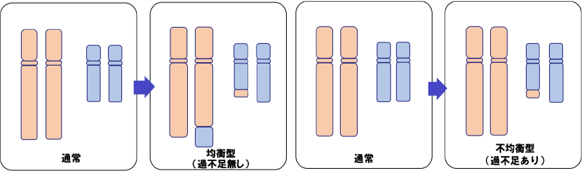
Chromosomal abnormality is a change in the genetic information called DNA, which is the blueprint of the human body. Normally, humans have 46 chromosomes, but chromosome abnormalities can be broadly classified into "number changes" and "structural changes.
For example, if there is one more chromosome 21, it is called trisomy 21(three chromosomes 21).
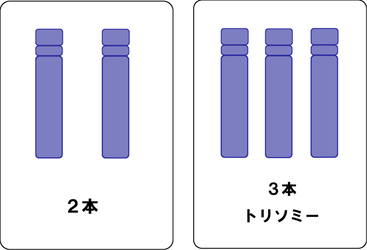
Chromosomes normally consist of 22 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Chromosomes with no excess or deficiency are called balanced chromosomes, while those with excess or deficiency are called unbalanced chromosomes.
Flow chart of chorionic tissue and amniotic fluid cell examination
What the QF-PCR method can tell us
The chorionic villi and amniotic fluid that are collected contain cells of fetal origin. DNA is extracted from these cells, and the QF-PCR method is used to check whether there are "number changes" in the fetus by limiting the test to chromosomes 21, 13, and 18, which are the most frequent chromosomal abnormalities, without culturing the cells.
In the QF-PCR method, DNA is extracted directly from the sample collected for testing, so test results can be provided as soon as five hours after the sample is collected or on the next clinic day.
* This test is a supplement to the chromosome test. Therefore, if the amount of chorionic villi or amniotic fluid collected is small, the QF-PCR test may not be performed because the chromosome test is prioritized.
What a G-band chromosome test (analog chromosome analysis) can tell you
The chorionic villi and amniotic fluid that are collected contain cells of fetal origin. These cells are cultured and examined for the shape and number of chromosomes to determine if the fetus has "chromosomal abnormalities".
Most changes in chromosome number and structure can be analyzed, but fine structural changes and changes at the genetic level cannot be detected. G-band analysis of trophoblastic cells and amniotic fluid cells may reveal chromosomal abnormalities after birth, even if normal chromosome results were obtained before birth, because band levels are inferior to those of postnatal blood samples.
Since chromosomal abnormalities account for only a small percentage of diseases in unborn babies, this test cannot detect all diseases. In addition, G-band cannot detect microchromosomal abnormalities, which have recently been discovered in many pediatric fields.
Even if chorionic villi or amniotic fluid are collected and cultured, the cells may not grow to a testable size and the results cannot be reported. (In CRIFM, there has never been a case of non-testability.
What the D-karyo test (digital chromosome analysis) can tell you
The chorionic villi and amniotic fluid that we collect contain cells of fetal origin. DNA is extracted from these cells, and using the NGS technique, we can examine the "change in number" and "change in structure" of all the chromosomes without culturing them.
The D-karyo test is performed by extracting DNA directly from the collected sample. This test uses the latest technology to determine chromosomal changes as waveforms.
Since chromosome testing uses a microscope, it is not possible to detect structural abnormalities that are difficult to distinguish with the human eye, depending on the cell type and proliferation ability. However, this technology can be used in combination to detect disproportionate "structural changes" that are considered undetectable by chromosome testing.
Since chromosomal abnormalities account for only a small portion of the diseases that babies are born with, this test cannot determine all diseases.
This test is only an adjunct to the chromosome test. Therefore, the results of the chromosome test will be comprehensive, including the results of the D-karyo test.
Prenatal diagnosis is the beginning of CRIFM Care
At CRIFM, we believe that prenatal diagnosis is not the goal, but the beginning.
If we find any abnormality in your baby, we will explain the condition of your baby based on objective and accurate imaging diagnosis. We will provide you with the latest information on the clinical course and treatment of each disease, which is advancing day by day, and we will discuss with you and your mother what preparations you can make for your baby.
CRIFM also provides consultation services for mothers and fathers who are unsure whether to continue their pregnancy or are worried about their ability to continue their pregnancy.
CRIFM does not deliver babies or provide treatment, but we will refer you to an appropriate medical institution based on the condition of the baby and the wishes of the mother and father.
The entire staff at CRIFM will support mothers and fathers in dealing with their babies until the end of their lives.
If you have any concerns about your baby, why don't you check the health of your baby with Dr. Pooh. Please feel free to call us first.
【attention】
The fetal diagnosis methods listed on this site are based on the diagnosis made by Dr. Pooh.
Please note that these diagnostic methods may not be the same as all diagnostic methods used at other facilities.
Medical appointments
All consultations are by appointment only. We accept all of them in principle. Appointments can be made by phone or by filling out the "Appointment Form" on our website.
Please remember to bring a letter of introduction written by the doctor who takes care of you, health insurance card, and maternal and child health handbook with you when you come to the clinic. If you do not have a letter of introduction, you will need to pay an additional fee of 5,500 yen (tax included).
Currently, in order to prevent coronavirus infection, only mothers are allowed to visit the clinic. Dads and other family members are asked to wait in the "Family Kizuna Lounge".
